Overview
Responsibilities
PPE Hazard Analysis
Selecting PPE
Head Protection
Eye and Face Protection
Foot Protection
Hand and Arm Protection
Fall Protection PPE
Electrical Protection PPE
Hearing Protection PPE
Respiratory Protection PPE
High Visibility Vests, Shirts, or Jackets
PPE when in the Field
PPE for Contract Workers
Training
Records

The purpose of this program is to protect our Yaskawa associates by ensuring that Personal
Protective Equipment (PPE) is provided, used, and maintained in a sanitary and reliable
condition whenever it is necessary due to hazards from processes or in the work
environment.
To the extent that it is possible and feasible, Yaskawa will remove or eliminate
hazards or exposures through engineering means to eliminate the need for PPE.
Note: The requirements outlined in this policy represent the minimum standards. Individual facilities or work areas may implement more stringent requirements; however, under no circumstances may they adopt standards that are less stringent than those stated herein.
The EHS Risk Mitigation Manager is responsible for:
The EHS Department conducts an analysis of the workplace to determine if hazards are present, or likely to be present, which necessitate the use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
This analysis consists of a survey of the workplace to identify sources of hazards to workers.
Consideration is given to hazards such as impact, penetration, laceration, compression (dropping heavy objects on foot, roll-over, etc.), chemical exposures, harmful dust, heat, light (optical) radiation, electrical hazards, noise, etc.
Where such hazards are present, or likely to be present, Yaskawa will:



All PPE clothing and equipment should be of safe design and construction, and should be maintained in a clean and reliable fashion.
Yaskawa takes the fit and comfort of PPE into consideration when selecting appropriate items for the workplace.
PPE that fits well and is comfortable to wear will encourage associate use of PPE.
Most protective devices are available in multiple sizes and care should be taken to select the proper size for each associate.
If several different types of PPE are worn together, Yaskawa makes sure they are compatible.
If PPE does not fit properly it may not provide the level of protection desired and may discourage employee use.
Hard hats are required any of the following apply:

There are two Types (impact protection) and three Classes (electrical protection) are recognized.
Type I head protection offers protection from blows to the top of the head.
Type II head protection offers protection from blows to the top and sides of the head.
| Class | Impact by flying and falling objects | Voltage Protection |
|---|---|---|
| A | Yes | Up to 2,200 Volts |
| B | Yes | Up to 20,000 Volts |
| C | Yes | None |

| Site | Hard Hat Required Areas |
|---|---|
| HQ |
|
| BG-A |
|
| BG-N |
|
| BG-Repair |
|
| BG-W |
|
| Franklin |
|
| Plain City |
|
| Solectria |
|
A daily inspection of the hard hat shell, suspension system and other accessories for holes, cracks, tears or other damage that might compromise the protective value of the hard hat is essential.
Hard hats with any of the following defects should be removed from service and replaced:
Hard hats shall be worn with the brim facing forward.
Approved hard hats shall be worn while working in a scissors or articulating lift when an overhead hazard is present or while working in close proximity to anyone working overhead.
Approved hard hats shall be worn while using a crane to lift items at or above head level.
See Electrical Safety PPE Section (8.0) for head protection for electrical work.
Eye protection is required whenever associates are exposed to eye hazards from flying particles, molten metal, liquid chemicals, acids or caustic liquids, chemical gases or vapors, potentially infected material or potentially harmful radiation.

Examples of potential eye hazards within Yaskawa America, Inc. include:
When face protection is required, the face shield shall be used in conjunction with approved safety glasses.
Face protection is required whenever associates are exposed to face hazards.
Examples of potential face hazards within Yaskawa America, Inc. include:

| Hazard Assessment Guidelines for Protective Eye and Face Wear | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Type | Examples of Hazard | Common Related Tasks | Eye | Face |
| Impact | Flying objects such as large hips, wire strands, wire bands, fragments, particles, sand, and dust | Wire cutting and stripping, soldering, electrical work, chipping, woodworking, sawing, drilling, powered fastening, riveting, and sanding Grinding, cutting metal bands |
YES | NO |
| Heat | Anything emitting extreme heat | Casting, hot dipping, welding, brazing | YES | YES |
| Chemicals | Splash, fumes, vapors, and irritating mists | Acid and chemical handling, decreasing, plating, working with adhesives | YES | YES |
| Dust | Harmful dust | Woodworking, buffing, and generally dusty conditions | YES | NO |
| Optical Radiation | Radiant energy, glare, and intense light | Welding, torch-cutting, and brazing Black light and laser work |
YES | NO |
| Safety Spectacles | Goggles | Specialty Safety Goggles | Face Shields | Welding Shields |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| These protective eyeglasses have safety frames constructed of metal or plastic and impact-resistant lenses. Side shields are available on some models. | These are tight-fitting eye protection that completely cover the eyes, eye sockets, and facial area immediately surrounding the eyes and provide protection from impact, dust, and splashes. Come in vented and non-vented. Some goggles will fit over corrective lenses. |
Laser Specialty goggles protect against intense concentrations of light produced by lasers. Ultra Violet (UV) (Black light) UV goggles also come in a UV safety spectacle. These are used while performing inspections under a black light. |
Transparent sheets of plastic extend from the eyebrows to below the chin and across the entire width of the head. Face shields protect against nuisance dusts and potential splashes or sprays of hazardous liquids but will not provide adequate protection against impact. Face shields must be worn in conjunction with safety spectacles or goggles. | Constructed of vulcanized fiber or fiberglass and fitted with a filtered lens, welding shields protect eyes from burns caused by infrared or intense radiant light. They also protect both eyes and face from flying sparks, metal spatter and slag chips produced during welding, brazing, soldering, and cutting operations. |
In addition to the specific tasks that require eye protection, Yaskawa America, Inc. has identified the following locations where safety spectacles are required:
| Site | Eye Protection Required Areas |
|---|---|
| HQ | Labs – while performing assembly, repair, or working with live electrical |
| BG-A |
All areas of production, except office desk area and aisles All product testing areas Machine Shop Parts cleaning stations Engineering Lab – while performing assembly, repair, or working with live electrical |
| BG-N |
All areas of production, including aisles, except office desk area All product testing areas Machine Shop Paint Booth Parts cleaning stations Repair – except office desk area Engineering Lab – while performing assembly, repair, or working with live electrical |
| BG-Repair |
All areas of repair,except aisles and office desk area All product testing areas Paint Booth Parts cleaning stations |
| BG-W | Warehouse – While building or destructing wood products Warehouse Bailer - While unloading bails and adding wire |
| Franklin |
All areas of production, except aisles All product testing areas – except office area when tests are not being performed Warehouse – except office desk area Labs – during active testing, assembly, repair, or working with live electrical |
| Plain City |
All product testing areas – except office desk area when tests are not being performed All product assembly areas – except aisles and office desk area Paint Booth Warehouse – while building or destructing wood products |
| Solectria |
All product assembly areas – except office desk area All product testing areas Warehouse – except office desk area Labs – while performing assembly, repair, or working with live electrical |

Associates who face possible foot or leg injuries from falling or rolling objects or from crushing or penetrating materials should wear protective footwear. Associates whose work involves exposure to hot substances or corrosive or poisonous materials must have protective gear to cover exposed body parts, including legs and feet. Associates exposed to electrical hazards must wear non-conductive footwear.

Examples of situations in which an associate should wear foot and/or leg protection include:

| Leggings | Metatarsal Guards | Toe Guards | Combination foot and shin guards | Safety Shoes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |


|
 |
 |
|
Protect the lower legs and feet from heat hazards such as molten metal or welding sparks. Safety snaps allow leggings to be removed quickly. |
Protect the instep area from impact and compression. Made of aluminum, steel, fiber or plastic, these guards may be strapped to the outside of shoes. |
Fit over the toes of regular shoes to protect the toes from impact and compression hazards. They may be made of steel, aluminum or plastic. |
Protect the lower legs and feet, and may be used in combination with toe guards when greater protection is needed. |
Impact-resistant toes and heat-resistant soles that protect the feet against hot work surfaces. The metal insoles of some safety shoes protect against puncture wounds. |
Electrically conductive shoes provide protection against the buildup of static electricity.
Foot powder should not be used in conjunction with protective conductive footwear because it provides insulation, reducing the conductive ability of the shoes.
Silk, wool and nylon socks can produce static electricity and should not be worn with conductive footwear.
Electrical hazard, safety-toe shoes are nonconductive and will prevent the wearers’ feet from completing an electrical circuit to the ground.
These shoes can protect against open circuits of up to 600 volts in dry conditions and should be used in conjunction with other insulating equipment and additional precautions to reduce the risk of an associate becoming a path for hazardous electrical energy.
The insulating protection of electrical hazard, safety-toe shoes may be compromised if the shoes become wet, the soles are worn through, metal particles become embedded in the sole or heel, or associates touch conductive, grounded items.

As with all protective equipment, safety footwear should be inspected prior to each use.
Shoes and leggings should be checked for wear and tear at reasonable intervals.
This includes looking for cracks or holes, separation of materials, broken buckles or laces.
The soles of shoes should be checked for pieces of metal or other embedded items that could present electrical or tripping hazards.
Associates should follow the manufacturers’ recommendations for cleaning and maintenance of protective footwear.
| Hazard Analysis Guidelines for Protective Footwear | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Type | Examples of Hazard | Common Related Tasks | Safety Shoes | Metatarsal | Electrical Hazard |
| Impact | Falling objects: drop object that is being carried, object falls off shelf | Assembly, repair, field service, material handling, building maintenance | YES | Optional | NO |
| Roll Over | Vehicle, pallet-jack, cart rolls over foot | Material handling, warehouse operations | YES | In some areas* | NO |
| Electrical | Electric Shock | Product troubleshooting and testing | YES | NO | YES |
| * Where identified in JHA | |||||
In addition to the specifications that require foot protection, Yaskawa America, Inc. has identified the following locations where safety shoes or toe guards are required:
| Site | Foot Protection Required Areas |
|---|---|
| HQ | Labs, Storage Cages, Shipping/Receiving Dock |
| BG-A |
All areas of production, except aisles and office desk area All product testing areas (Electrical Hazard) Machine Shop Parts cleaning stations Engineering Lab Warehouse |
| BG-N |
All areas of production, except aisles All product testing areas (Electrical Hazard) Warehouse |
| BG-Repair |
All areas of repair, except aisles and office desk area All product testing areas (Electrical Hazard) Machine Shop Warehouse |
| BG-W | Warehouse All areas of production, except aisles and office desk area All product testing areas (Electrical Hazard) Repair |
| Franklin |
All areas of production, except aisles All product testing areas (Electrical Hazard) Shipping, Receiving, Parts Kitting Areas Labs Machine Shop |
| Plain City |
All product testing areas (Electrical Hazard) All product assembly areas – except aisles and office desk area Paint Booth Warehouse |
| Solectria |
All product assembly areas All product testing areas (Electrical Hazard) Warehouse Labs |

Hand and arm protection is required when potential injury to hands and arms cannot be eliminated through engineering and work practice controls. Potential hazards include skin absorption of harmful substances, chemical or thermal burns, electrical dangers, bruises, abrasions, cuts, punctures, fractures and amputations. Protective equipment includes gloves, finger guards and arm coverings or elbow-length gloves.

Protective Gloves
The nature of the hazard and the operation involved will affect the selection of gloves.
The variety of potential occupational hand injuries makes selecting the right pair of gloves challenging.
It is essential that employees use gloves specifically designed for the hazards and tasks found in their workplace because gloves designed for one function may not protect against a different function even though they may appear to be an appropriate protective device.
The following are examples of some factors that may influence the selection of protective gloves:
Insulating Rubber Gloves have an untested shelf life of 1 year
Once used, insulating rubber gloves must be re-certified every 6 months
Cost center manager is responsible for sending the gloves for recertification

| Hazard Assessment Guidelines for Protective Hand and Arm Ware | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Type | Examples of Hazard | Common Related Tasks | Required | Type |
| Sharp Edges/Items | Sharp edge of sheet metal, burr on sheet metal, knife blade | Assembly, repair, facility maintenance | YES* | Leather, canvas, metal mesh |
| Slivers, chafing, abrasions | Rough, sharp, or heavy materials | Assembly, repair, facility maintenance | YES* | Fabric or Leather |
| Chemical burns | Using a chemical harmful to skin | Using caustic chemical | YES | As required in Safety Data Sheet |
| Electrical | Electric Shock/Burns | Product troubleshooting and testing | YES | Proper voltage rated insulated gloves. Long sleeves as required by NFPA 70E |
| * Where identified in JHA | ||||
Protective gloves should be inspected before each use to ensure that they are not torn, punctured or made ineffective in any way.
A visual inspection will help detect cuts or tears but a more thorough inspection by filling the gloves with water or air and tightly rolling the cuff towards the fingers will help reveal any pinhole leaks.
Gloves that are discolored or stiff may also indicate deficiencies caused by excessive use or degradation from chemical exposure.
Any gloves with impaired protective ability should be discarded and replaced.
Reuse of chemical-resistant gloves should be evaluated carefully, taking into consideration the absorptive qualities of the gloves.
A decision to reuse chemically-exposed gloves should take into consideration the toxicity of the chemicals involved and factors such as duration of exposure, storage and temperature.
Insulating Rubber Gloves have an untested shelf life of 1 year.
Once used, insulating rubber gloves must be re-certified every 6 months.
Cost center manager is responsible for sending the gloves for recertification.
When guardrails and other positive fall protection are not available to protect from falls, associates working at heights greater than 4’ above lower level, or where a fall into live electrical parts or operating machinery is a hazard, associates must use personal fall protection systems such as harnesses, lanyards, and lifelines.
Training Requirements
Before use, associates must be trained to understand:
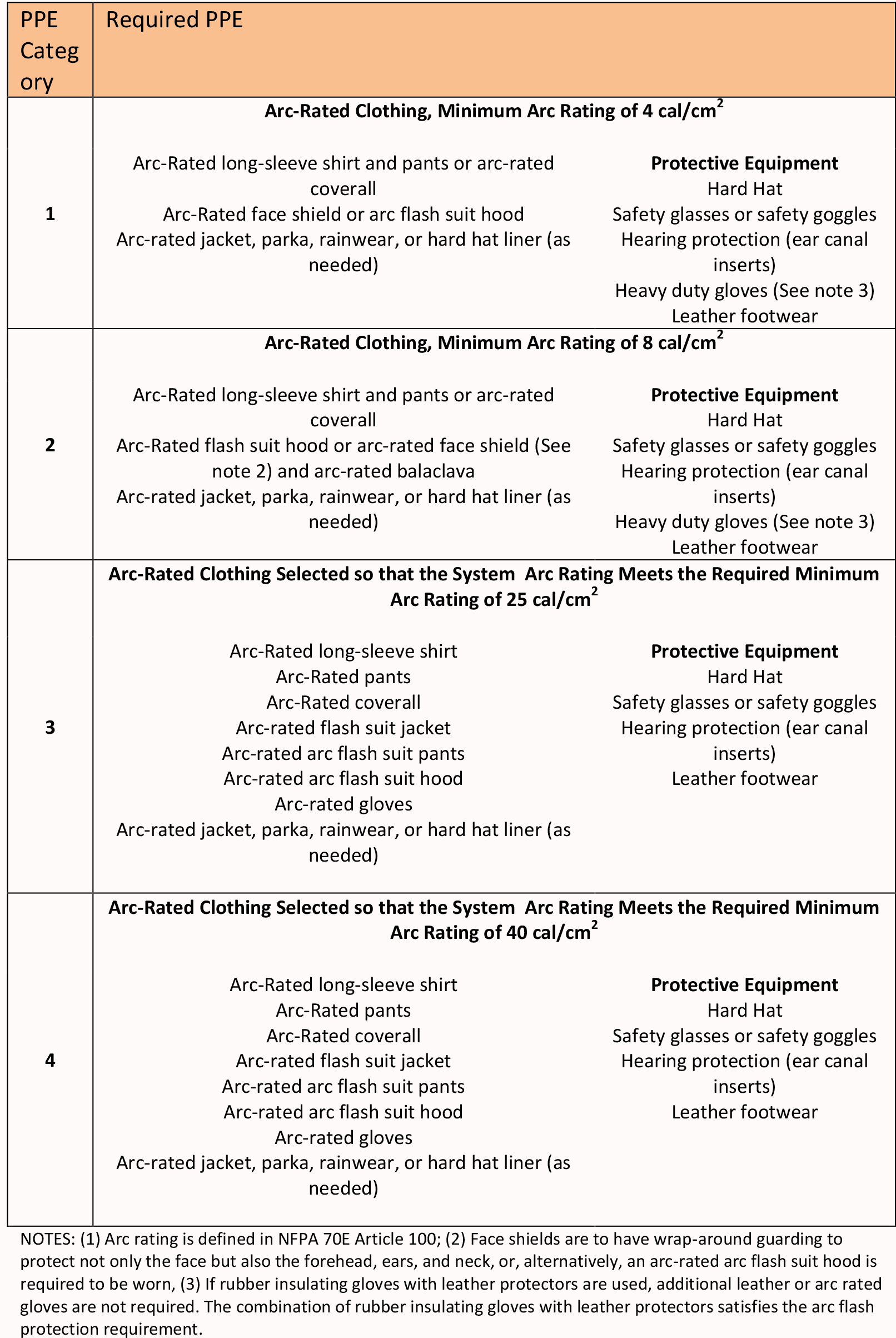
When the arc rating is below 1.2 cal/cm2, the following PPE is required:
Ear Plugs
Ear plugs are inserted to block the ear canal. They may be premolded (preformed) or moldable (foam ear plugs).
Ear plugs are sold as disposable products or reusable plugs. Custom molded ear plugs are also available.

Semi-Insert Ear Plugs (Ear Caps)
Semi-insert ear plugs which consist of two ear plugs held over the ends of the ear canal by a rigid headband.

Ear Muffs
Ear muffs consist of sound-attenuating material and soft ear cushions that fit around the ear and hard outer cups. They are held together by a head band.

Yaskawa provides hearing protection at no cost to:
| Permissible Noise Exposures | |
|---|---|
| Duration per day, hours | Sound level dBA slow response |
| 8 | 90 |
| 6 | 92 |
| 4 | 95 |
| 3 | 97 |
| 2 | 100 |
| 1 ½ | 102 |
| 1 | 105 |
| ½ | 110 |
| ¼ or less | 115 |
Personal Protective Equipment for Respiratory protection is addressed in Yaskawa's Respiratory Protection Policy.
Medical examinations shall be required for any associate prior to assignment to any job which requires use of a respirator. No associate with respiratory disease or other medical limitations will be allowed to perform work in areas requiring the use of respiratory equipment.
All medical evaluations will be confidential, during normal work hours, convenient, understandable and the associate will be given the opportunity to discuss the results with the examining physician or health care provider.
A medical evaluation is not required for voluntary use of a dust mask (e.g. N95 mask). All
Where high visibility garments are required, they shall comply and be labeled with ANSI/ISEA 107 Class 2 or Class 3. High visibility vests must be fully zipped or fastened to provide the required 360° visibility. An open vest reduces the protective surface area below the ANSI threshold.
The background material color shall be one of the approved fluorescent colors:
High-visibility garments—such as vests, shirts, or jackets—must be worn in warehouse areas and in any location designated as requiring high-visibility apparel.
Yaskawa may provide high-visibility jackets or sweatshirts to associates working in cold environments, such as while loading or unloading trailers in the warehouse.
High-visibility jackets, shirts, or sweatshirts shall not have hoods, as hoods can restrict a person’s field of vision.
Yaskawa associates working in the field shall follow the more restrictive PPE policy between the requirements defined in this policy and the customer’s PPE requirements.
Yaskawa will inform contract employers of the PPE requirements.
The Contract Employer shall provide the following PPE:
General PPE training is included in Safety Orientation Training. Records are maintained in Yaskawa’s Learning Management System.
Hands-on Eye and Face Protection, Foot Protection, Hand and Arm Protection, Hearing Protection, and Head Protection PPE training is provided by the associate’s supervisor prior to first use. No records are required.
Fall Protection PPE training is provided by a qualified Fall Protection trainer prior to the associate’s first use of fall protection PPE.
Records are maintained by the associate's supervisor.
Electrical Safety Protection is provided by a qualified Electrical Safety trainer prior to the associate’s first use of electrical safety PPE.
Respiratory protection PPE training is provided by a qualified trainer.
| Record Title | Retained by | Disposition |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Protective Equipment Training Records | Maintained by Supervisor or Yaskawa's Learning Management System | Employment Tenure plus 5 Years |
| Job Hazard Assessment | Electronically Available to All Associates, stored on Network Computer or www.YaskawaSafety.com website | Retained while process is active |
| Rev # | Description | Release Date | Approved by |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Conversion of old safety documents, rewrite, and issue | 5/17/2016 | Thurwanger |
| 1 | Added flowcharts | 10/12/2016 | Thurwanger |
| 2 | Added BG-W warehouse (was previously BG-A) | 5/24/2019 | Thurwanger |
| 3 | Changed Learning Management System from SuccessFactors to UKG Learning | 2/12/2022 | Thurwanger |
| 4 | Added Franklin Drive Value Add facility, Removed Oak Creek | 6/12/2025 | |
| 5 | Add requirements that high visibility vests must be fully zipped or fastened | 2/11/2026 | Thurwanger |
| Review Date | Reviewed by | Changes Required (Yes/No) | Revision # if updated |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2/21/2017 | Thurwanger | No | |
| 1/16/2018 | Thurwanger | No | |
| 1/22/2019 | Thurwanger | Yes | 2 |
| 1/14/2020 | Thurwanger | No | |
| 1/21/2021 | Thurwanger | No | |
| 1/18/2022 | Thurwanger | Yes | 3 |
| 1/31/2023 | Thurwanger | No | |
| 1/16/2024 | Thurwanger | No | |
| 1/21/2025 | Thurwanger | Yes | 4 |
| 2/11/2026 | Thurwanger | Yes | 5 |
Policy Video
